水资源管理与气候变化
中国金沙江流域:通往成功的路上
了解更多关于气候变化与社会经济发展对水资源的影响,以及如何采用适当的工具与产品制定适应性措施的全面规划,从而有助于地区长期持续发展。探讨在中国实施的中瑞合作金沙江流域项目。
Scroll Down 工具与产品了解更多关于气候变化与社会经济发展对水资源的影响,以及如何采用适当的工具与产品制定适应性措施的全面规划,从而有助于地区长期持续发展。探讨在中国实施的中瑞合作金沙江流域项目。
Scroll Down 工具与产品长江流域是中国的社会经济重地,金沙江位于长江的上游。在过去的二三十年里,金沙江流域经历了气候变暖以及日益增加的极端气候事件,如洪旱灾害等,对当地造成了重大经济损失。同时,工业、居民区、水电、农业、生态系统和旅游等不同行业和利益相关者对水资源与气候变化非常敏感。
瑞士和中国合作开展的金沙江项目,旨在为提高金沙江流域水资源管理能力、成功应对气候变化与经济社会发展奠定坚实的基础。丽江位于云南省西北部,是金沙江项目的试点地区,现已对其当前的水资源状况及趋势进行了分析。瑞士和中国已在水资源管理和气候变化领域合作了十多年。两国在水资源方面都受到了气候变化的严重影响。
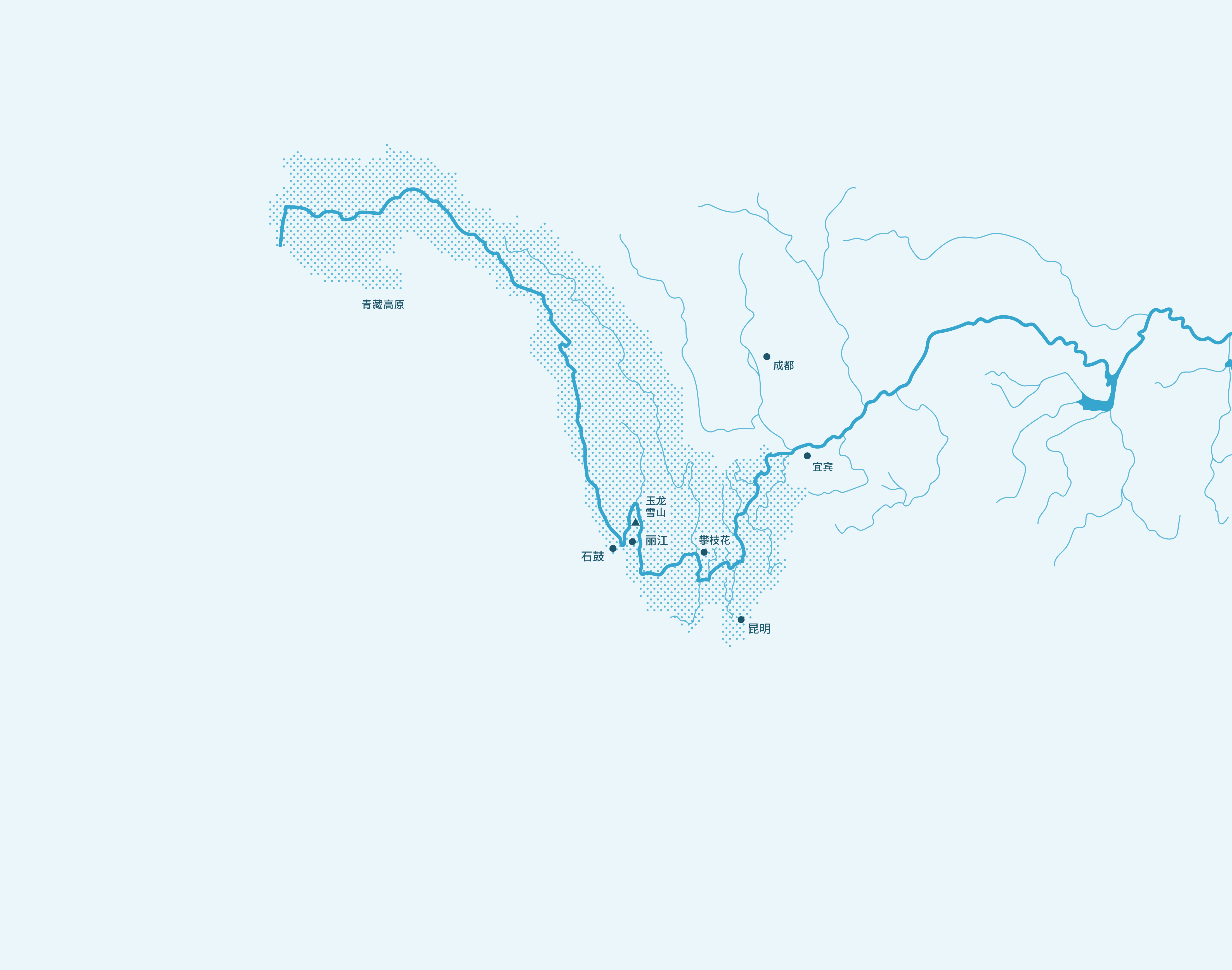
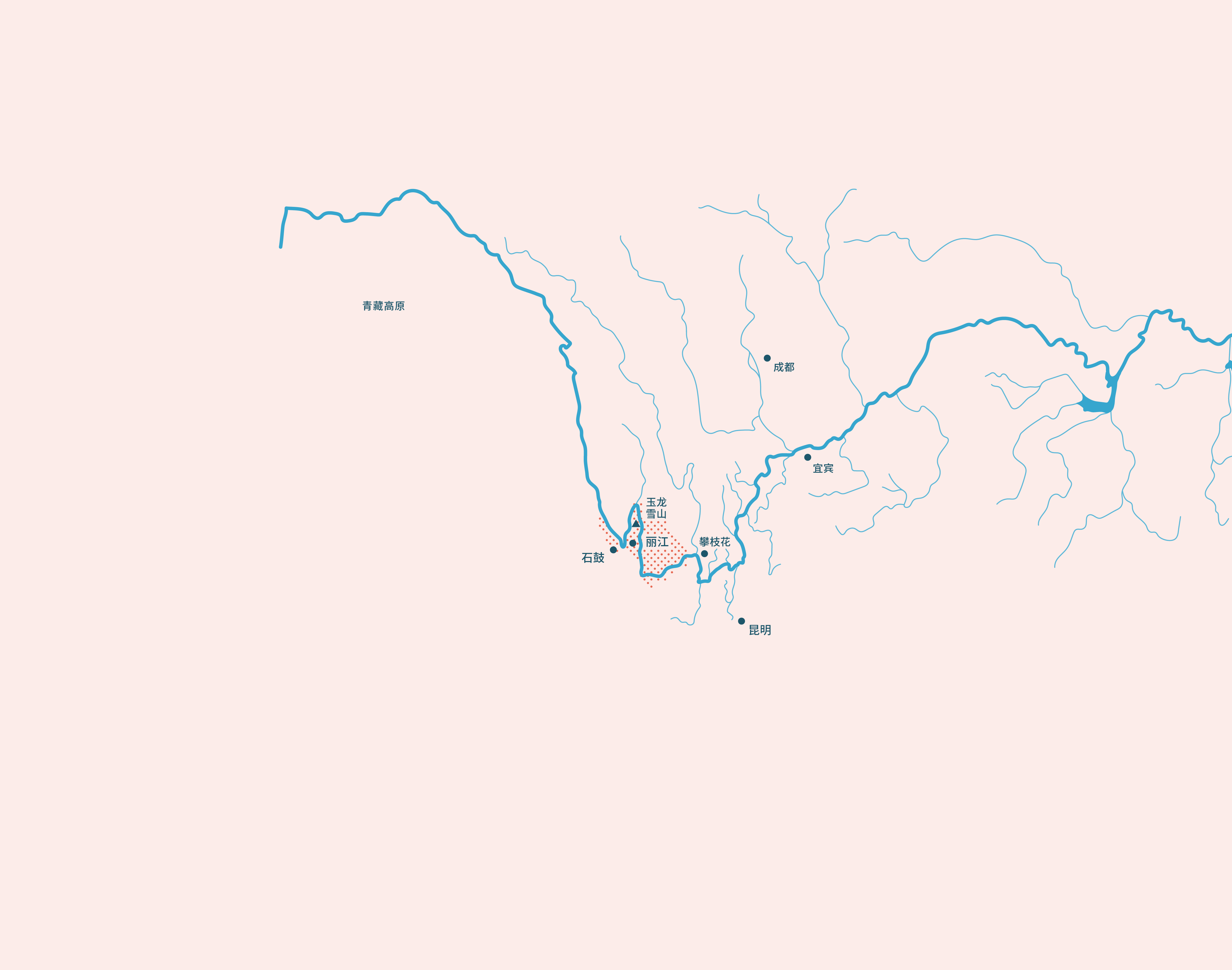
请使用地图来了解金沙江流域!
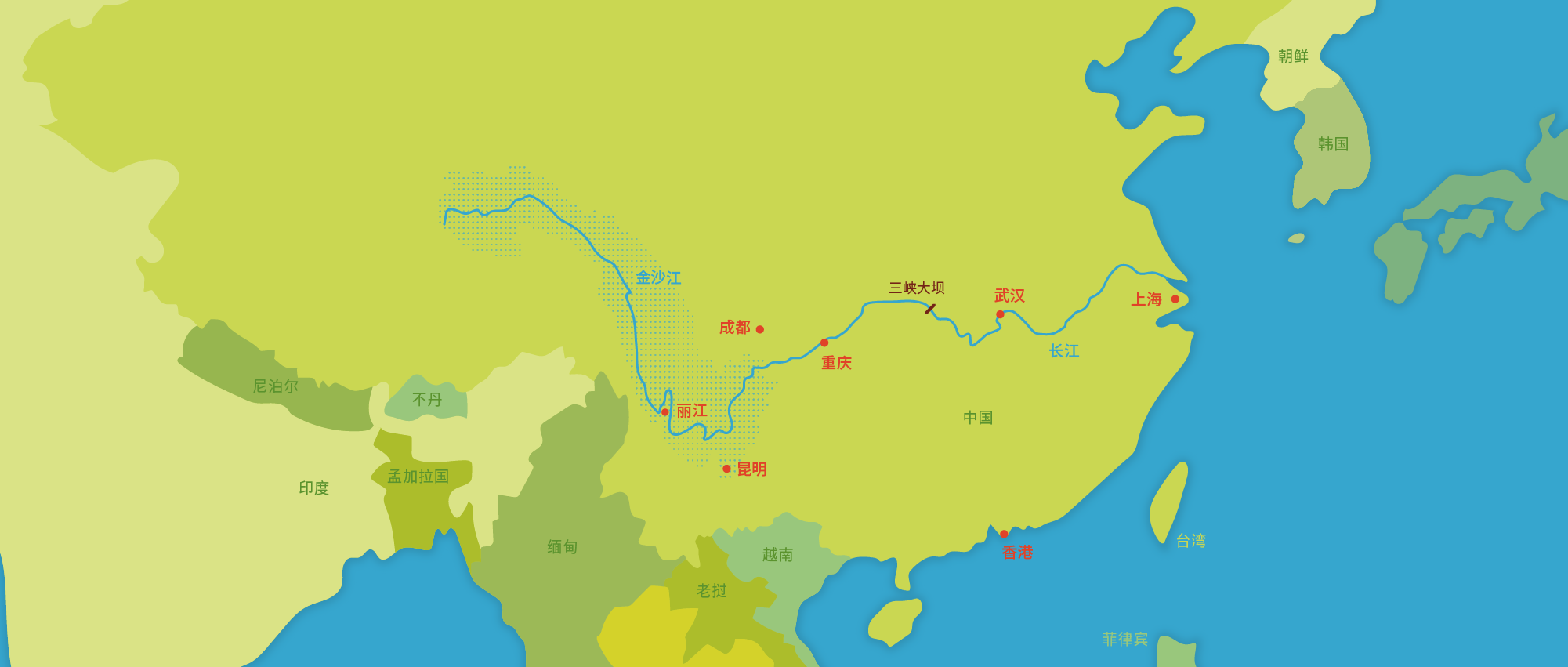
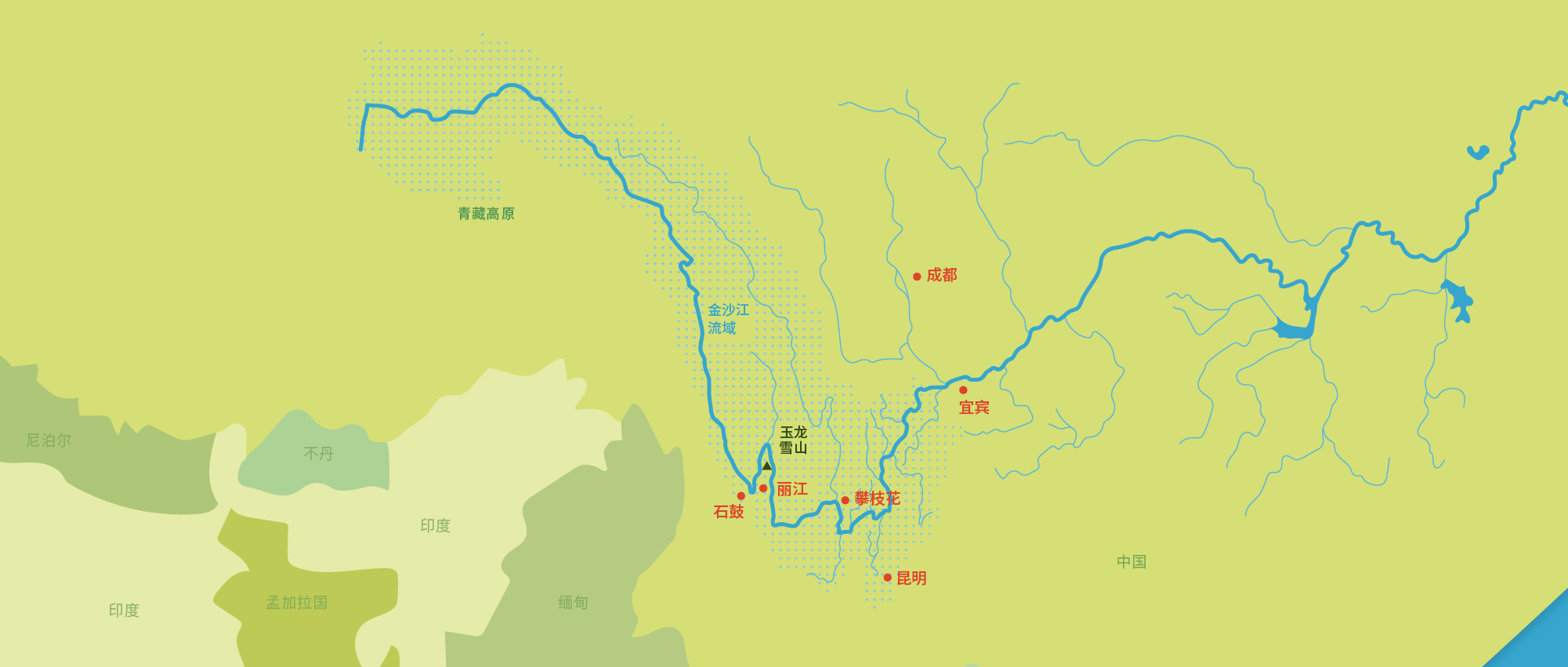
金沙江的源头位于青藏高原,主要穿过中国西南地区的青海省、云南省和四川省。金沙江的流域面积占长江流域面积的26%。
长江是中国第一长河,也是世界第三大河,河长超过6000km。长江流域面积达170万km² ,流经大约五分之一的中国领土。
冰川融雪径流和气候变化对金沙江流域的水文状况影响很大。近年来,极端气候事件如洪涝灾害频发。气候变化对水资源和生物多样性有较大影响。
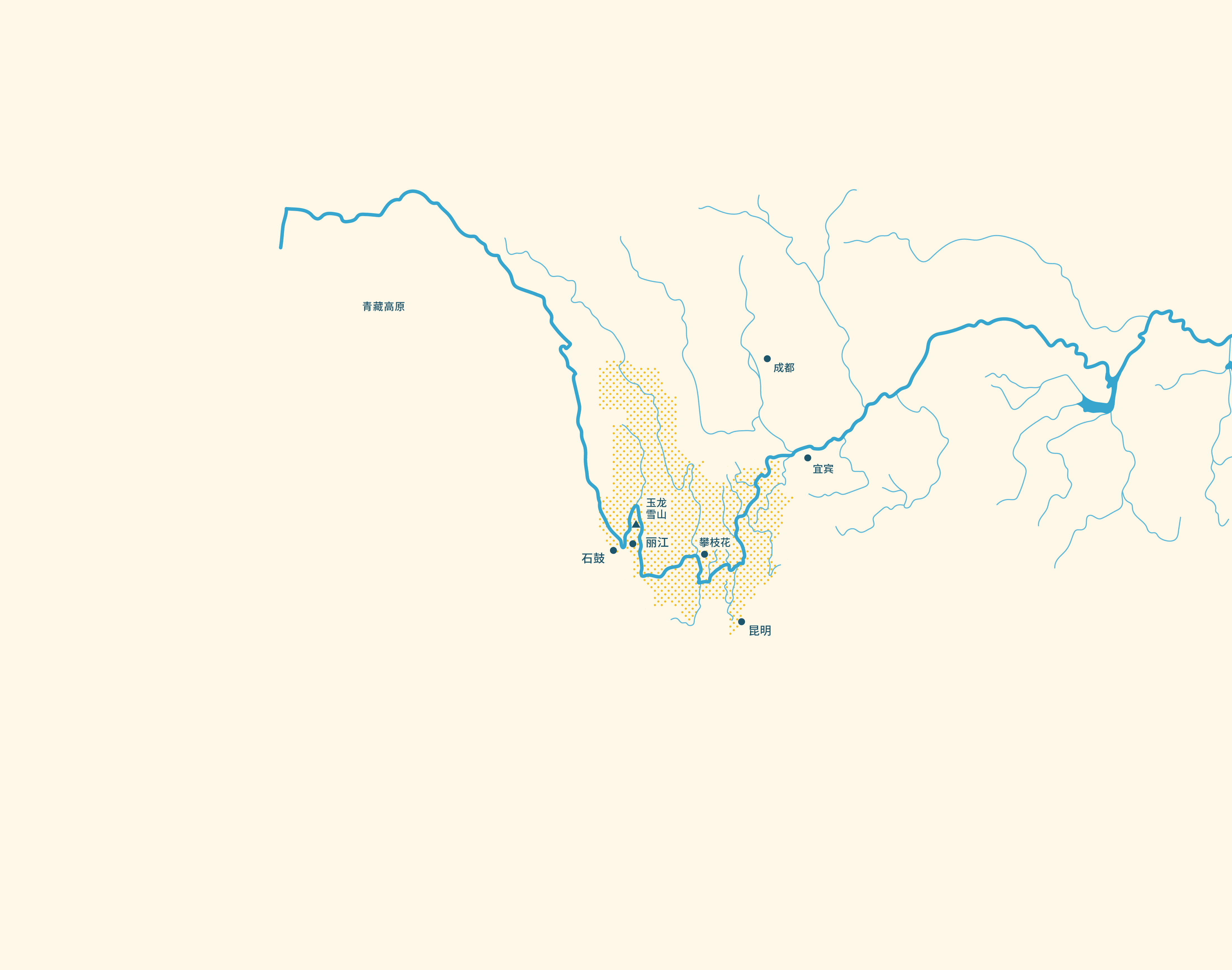
丽江市是本项目的试点地区,在过去的二三十年里面临着日益严重的水资源危机:泉水与河道已开始干涸,河流生态日益恶化。同时,各行业需水也不断增长,尤其是农业和旅游业。
冰川是水循环的重要组成部分。 近年来玉龙雪山冰川严重退化, 因此,对其现状和变化趋势的观测十分必要。
本项目的长期目标为,基于气候变化与社会经济发展,提高金沙江流域水资源的综合管理。从而有效地保护生命和财产,保障该地区的水资源安全,为中国经济的可持续发展以及探讨全球水资源与气候变化做出贡献。
项目第一阶段为三年,旨在为金沙江流域未来水资源综合框架奠定基础。因此,主要目标如下:
在金沙江流域,不同行业和利益相关者都受到气候变化与社会经济发展的影响。如今,所有行业和利益相关者都对水资源有很强的依赖。金沙江项目旨在让这些行业的水资源供给与需求在未来达到可持续的平衡。

金沙江流域及整个中国在都市化与人口增长方面都显现了强劲的趋势。日益增加的城市居民导致了更高的水资源需求与消耗。对水资源的供给与需求进行合理、可持续的管理,将能缓解紧张的局面及冲突。
更多

该地区主要以农业发展为主。烟草是云南省和四川省主要的出口产品。绝大多数的农村居民主要靠农业维持生计,受到旱涝的影响较大。考虑到传统灌溉需水量大,本项目将会一定程度考虑影响他们的生活需水等情况。
更多

本地区计划进行大量的水电站投资。沿着金沙江流域的干流及雅砻江,已经规划了42座梯级水电站,而且部分电站已经建成,这将会影响整个流域的水文情势。一些气候情景预测未来的水资源量可能会减少,因此水力发电产也会减少。本项目将有助于优化水电站调度规则,从而满足所有用水行业的需求。
更多

人类在很多方面都受益于生态系统。该地区的生态系统能保证重要的服务功能,如防洪、水净化、鱼类栖息地以及文娱功能。气温、降水变化在很大程度上影响生态系统,而后者会对人类造成负面影响。适当的水资源管理可以起到预防作用。
更多

该地区主要的制造业为重工业,如煤炭、铁矿、钢和铜生产。这些工业发展迅速,它们的生产工作在很大程度上依赖于水资源。适当的水资源管理则能保证这些用户的用水,且能管控水污染风险,这对其他用水户来说至关重要。
更多

在金沙江流域,旅游业是一个持续发展的行业,特别是在丽江地区。丽江的古镇已被联合国教科文组织认定为世界文化遗产。未来旅游业将有较高的用水需求。本项目旨在使该地区的水资源供给与需求达到可持续的平衡。
更多
为了改善水资源综合管理,我们增进了对金沙江流域现状水资源特征、极端气候事件和水生态系统的充分了解。以现状为基准年,识别气候变化和社会经济发展对水资源及极端水文事件的影响。从而制定了适应策略和措施。探索我们的工具和产品!
了解更多

了解更多
了解更多

了解更多
了解更多

了解更多
项目开发了气象水文数据分析软件,该软件可以深入分析气温和降水观测值的历史变化趋势,分析结果表明温度增加趋势明显。
项目开发了一个灾害事件登记平台,该平台可以记录,可视化和分析异构灾害事件数据。主要的灾害信息如受灾人员、受灾面积和经济损失等都可登记。
基于遥感监测数据,项目组对金沙江流域上游的积雪覆盖和融雪径流过程进行模拟分析。
项目组基于金沙江水系 50 多个站点的实测数据构建了水文预报模型,该模型可用于支持防洪决策制定,从而提高洪水预警和水库调度水平。
对于金沙江下游地区,近期和远期气温预测分别增加约 1 – 2° C和 1.5 – 5° C。多数气候情景预测上游和中游地区的降雨未来呈现增加趋势,下游地区降雨变化存在一定不确定性。
为了模拟未来气候变化,确定了8 套近期气候情景 (2021 – 2050)和16 套远期 (2070 – 2099)的逐日气温和降水数据。
基于气候情景数据,项目组分析气候变化对水力发电、农业、洪旱事件以及水生态系统的影响。
气候变化引起的水温升高是影响冷水鱼栖息地的重要因素之一,然而,由于水库大坝的修建将鱼类在不同生长期迁徙至适宜栖息地的路径阻断,水电站的运行对鱼类生境的影响较气候变化影响更大。
随着降雨量和温度的增加,作物种植适宜区面积预期会增加,向北和高海拔地区迁移。然而,作物的需水量也会增加。
年均径流和丰水期径流预期会增加,但受限于发电装机容量,水力发电量并不会按比例 增加。
本项目制定了应对洪水、农业和洪旱事件的示范措施,以及选定地区的农业和水文干旱事件,并分析了受影响部门和利益相关方面临的挑战。
项目组基于金沙江水系 50 多个站点的实测数据构建了水文预报模型,该模型可用于支持防洪决策制定,从而提高洪水预警和水库调度水平。
监测站可以提供分析气候变化对冰川融化和径流的影响的基本数据。通过实时监测,首次实现玉龙雪山冰川变化的可视化。
丽江的水危机日益严峻,枯水时段表现尤为严重。农业灌溉需水未来预计增加 3% 到 7% 。由于未来城市化进程和旅游业的快速发展,未来城镇需水预计增加一倍。
项目构建的水资源评估与规划模型,可以再现丽江市现状和未来供需水状况。通过评估 52 项适应性措施来缓解丽江水危机,这项成果将用于当地水管理部门的规划制定过程。
你想知道更多关于金沙江流域项目的信息吗?请查看该项目的会议介绍或阅读我们的出版物:


概念、内容&网页设计
EBP Schweiz AG
Cornelia Büttner + Monika Rohner
Zollikerstrasse 65
CH-8702 Zollikon
kommunikation@ebp.ch
www.ebp-kommunikation.ch
技术实施
Odoson
Robert Baumgartner
Carrer d’Ali Bei 7, 2-2
ES-08010 Barcelona
hello@odoson.com
www.odoson.com
版权
© 2017 EBP
制责任限
本公司已采取一切合理的努力,确保网站的内容在编制时是正确的。然而,EBP Schweiz AG并不能保证第三方信息的准确性。其他网站的链接不在EBP Schweiz AG的控制之内。